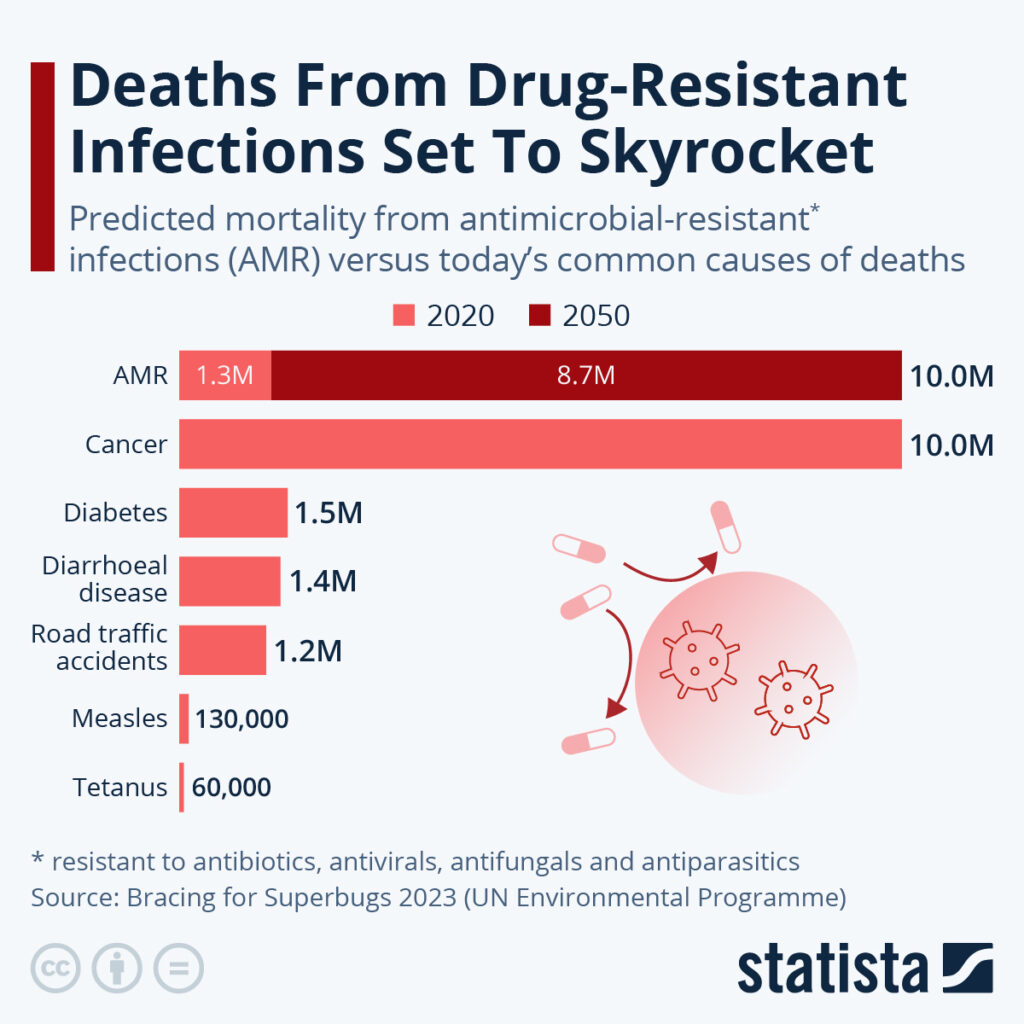
April 2025 — A recent study has revealed that drug-resistant child deaths are emerging as a critical global health crisis. New research presented at ESCMID Global 2025 in Vienna shows that while some models estimate over 3 million child deaths in 2022 from antimicrobial resistance (AMR), more conservative figures point to several hundred thousand. Regardless of the exact number, the impact is severe.
Understanding Drug-Resistant Child Deaths
Variations in estimates arise from different methodologies and data sources. Some experts, using broad modeling approaches, reach figures as high as 3 million child deaths, whereas routine surveillance and WHO data report numbers in the hundreds of thousands. The burden of these infections on children is an urgent public health issue.
Key Findings on AMR Impact
- Global Impact: One study estimated over 3 million child deaths in 2022 might be linked to drug-resistant infections, while other analyses indicate several hundred thousand.
- Regional Disparities: Areas such as Southeast Asia and Africa face a heavier burden due to limited healthcare infrastructure and poor sanitation.
- Antibiotic Misuse: The inappropriate use of high-risk “Watch” and “Reserve” antibiotics accelerates the development of resistant infections.
Factors Contributing to Drug-Resistant Child Deaths
The following factors intensify this crisis:
- Overcrowded Healthcare: Limited resources and high patient loads facilitate the rapid spread of resistant infections.
- Poor Sanitation: Inadequate hygiene measures increase pathogen transmission.
- Lack of Diagnostics: Without rapid, accurate tests, clinicians often use broad-spectrum antibiotics, driving resistance further.
- Inappropriate Antibiotic Use: Overprescription or misuse contributes significantly to the rise in resistance.
Urgent Actions to Fight AMR
The findings underscore an urgent need for global intervention:
- Strengthen Healthcare Systems: Improve infection prevention and control measures.
- Enhance Surveillance: Implement robust systems to track antibiotic use and resistance patterns.
- Promote Responsible Antibiotic Use: Educate healthcare providers and the public on proper usage.
- Invest in Research: Accelerate the development of new antibiotics and alternative treatments.
Conclusion
Whether models estimate several hundred thousand or over 3 million child fatalities annually, the threat of drug-resistant child deaths is undeniable. Strengthened global cooperation, improved data collection, and decisive public health strategies are essential to protect future generations.
Note: Figures cited vary by study. Ongoing research and improved surveillance are necessary to fully assess the impact of antimicrobial resistance on child mortality worldwide.
Learn more about antimicrobial resistance from the World Health Organization.